Extreme Heat
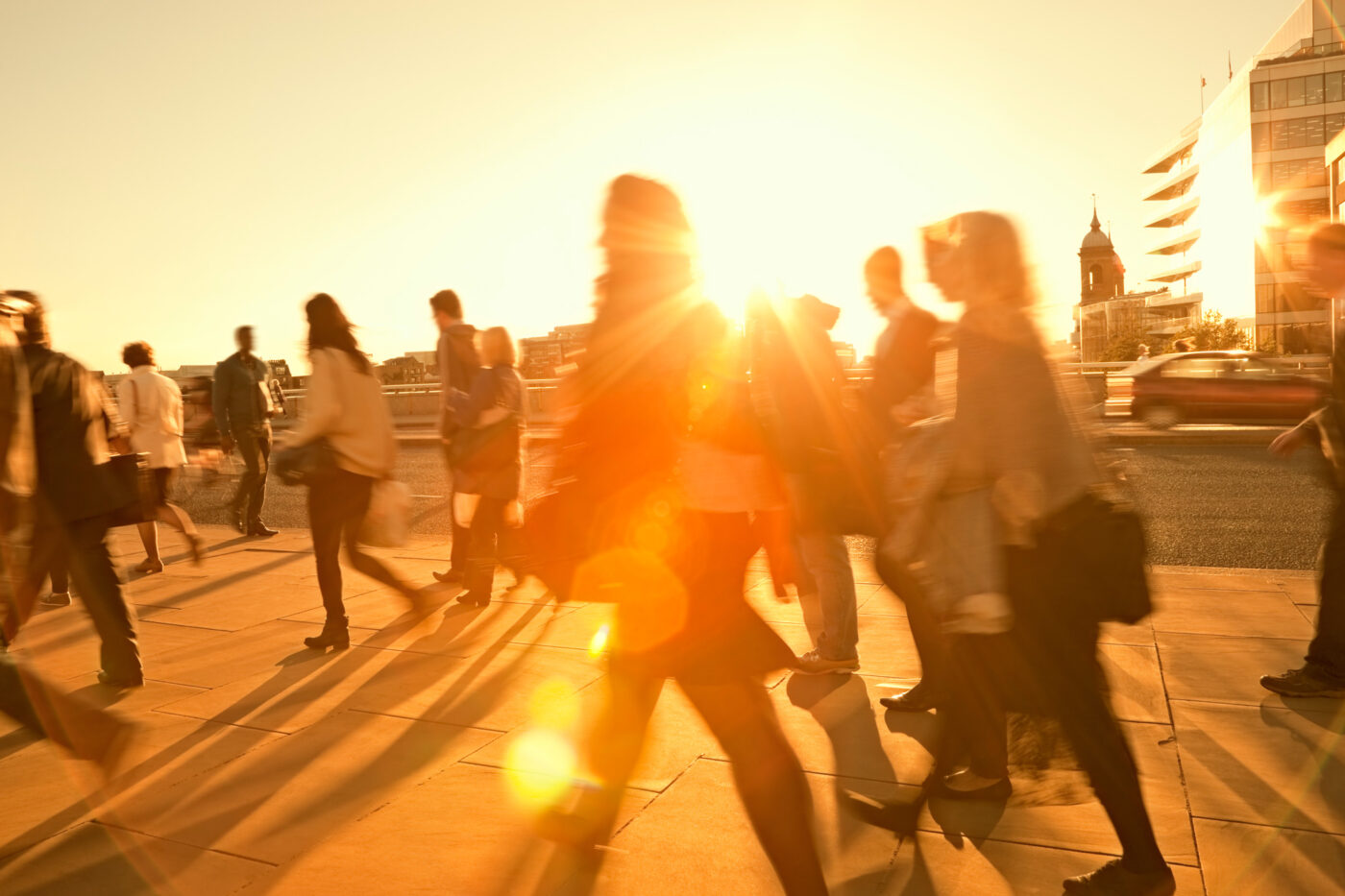

Extreme heat occurs when exceptionally hot and humid weather persists for more than two days and exceed the historical norms for a region. These extreme heat events put enormous stress on our bodies, which may directly cause heat stroke or heat stress and indirectly exacerbate chronic conditions.
Wildfire and Wildfire Smoke
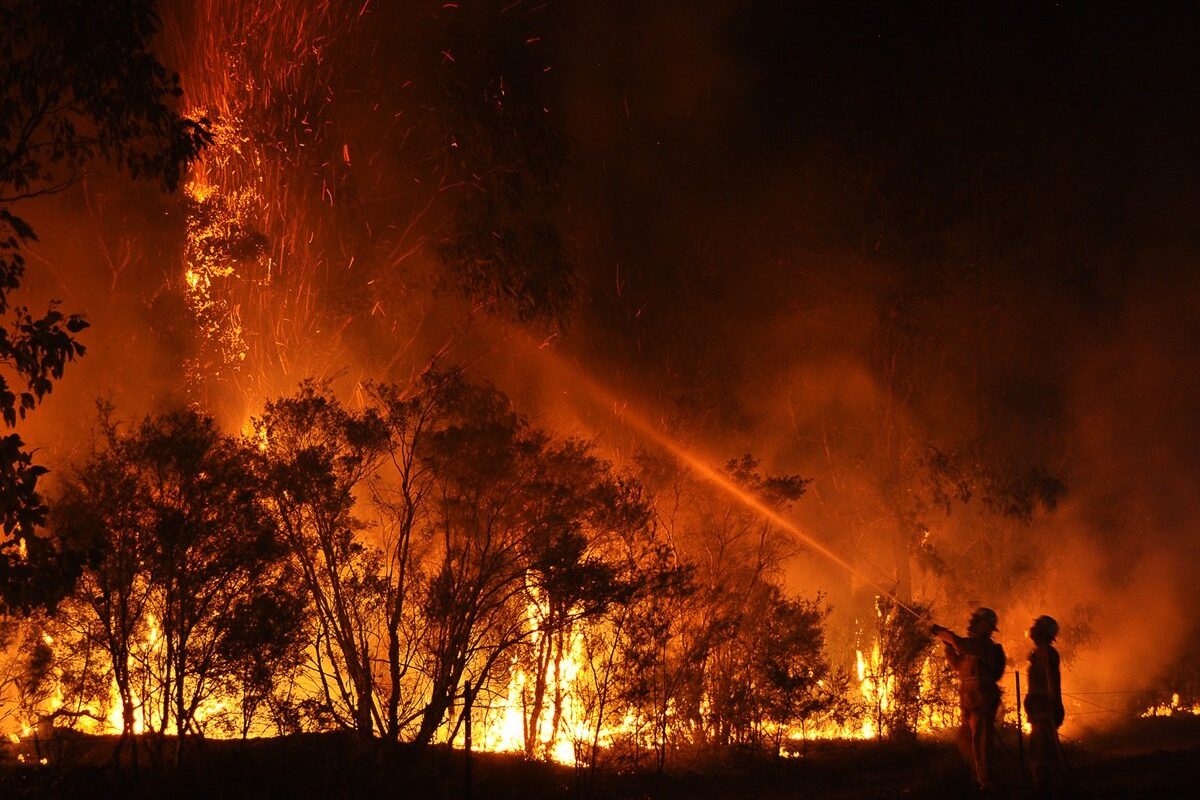

Wildfire is an unplanned, uncontrolled fire burning in a natural area. Wildfires can directly cause immediate human casualties and displacement of affected communities, and indirectly produce high levels of air pollution, which can influence the respiratory and cardiovascular health of the immediate community and distant regions, alike.
Drought
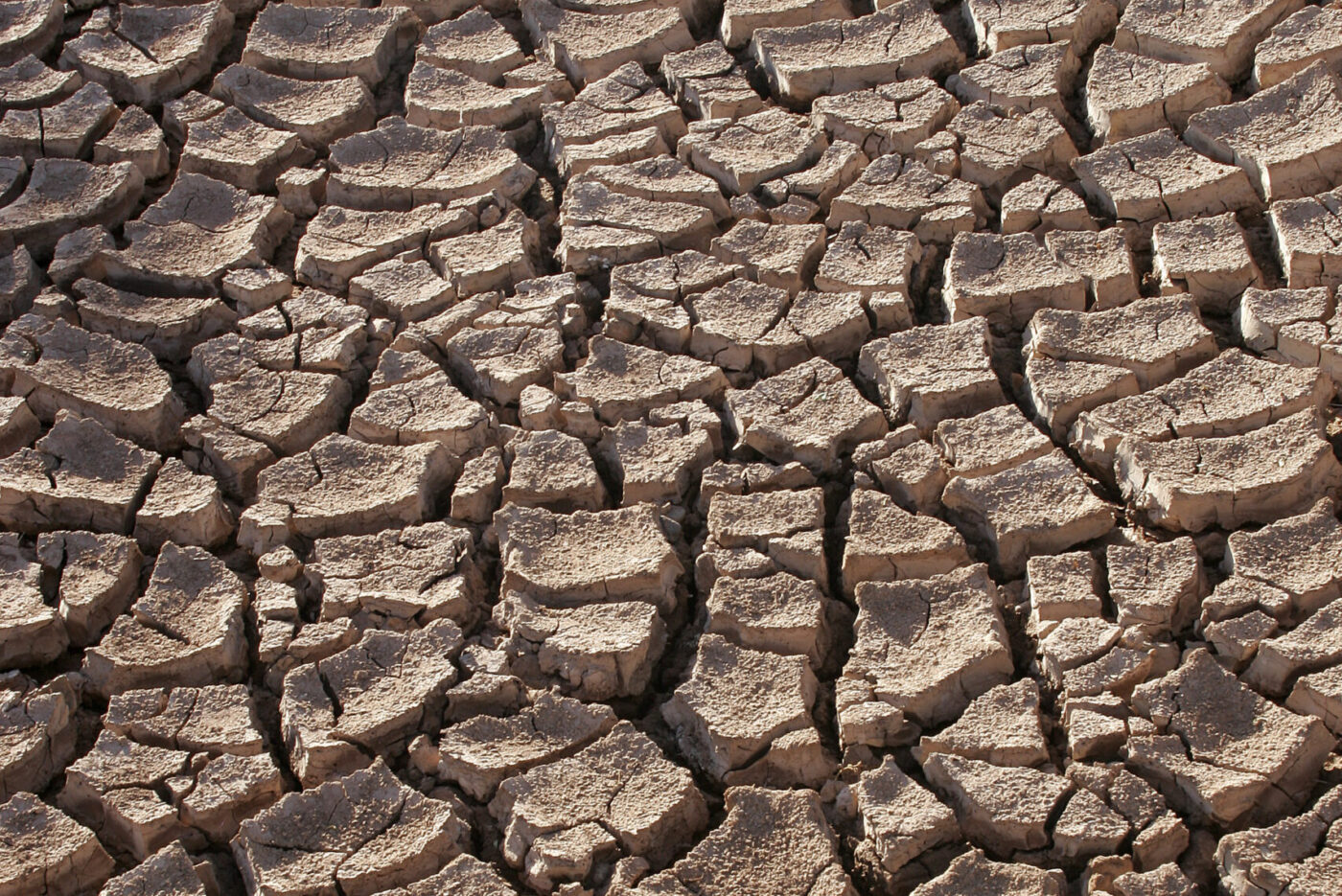

Drought describes abnormally dry weather conditions for a region. Due to the great influence of water in the environment and the socio-economic role of water, the health impacts of droughts span from chronic disease aggravation to infectious disease augmentation, to mental and societal unrest.
Flooding
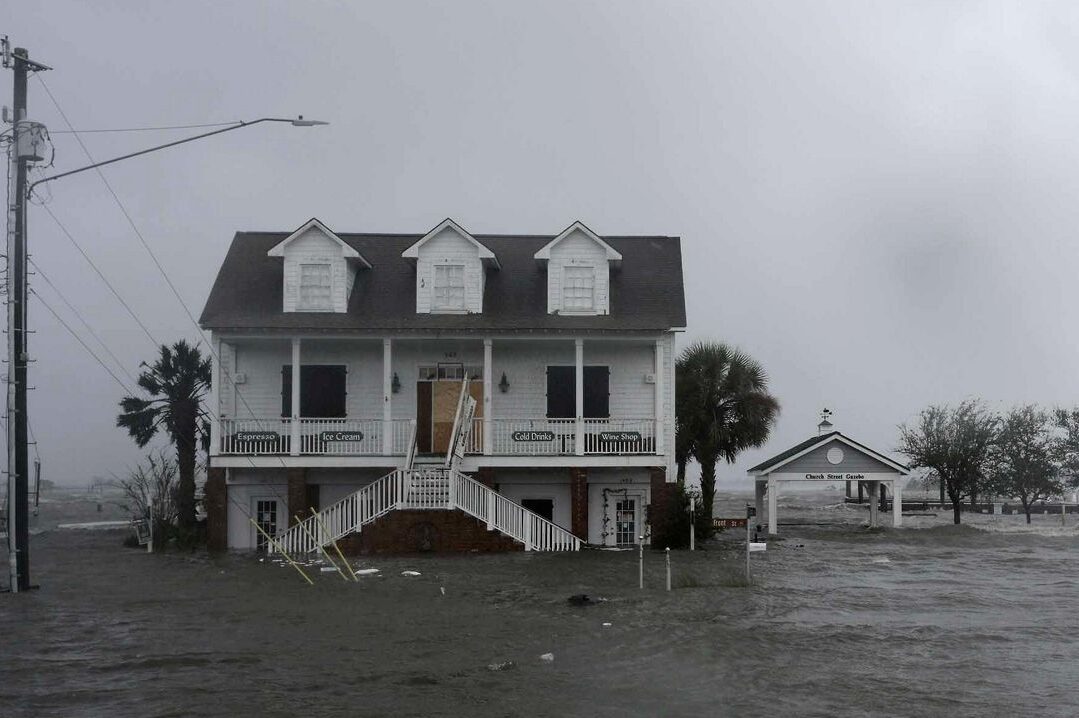

Flooding occurs along the coast and along riverbanks due storm events or anthropogenic climate change trends. Flooding of homes or other community structures impact both our physical and mental health through mold growth, accelerated spread of infectious disease, disruption of community, and displacement of people.
Greenness (NDVI)
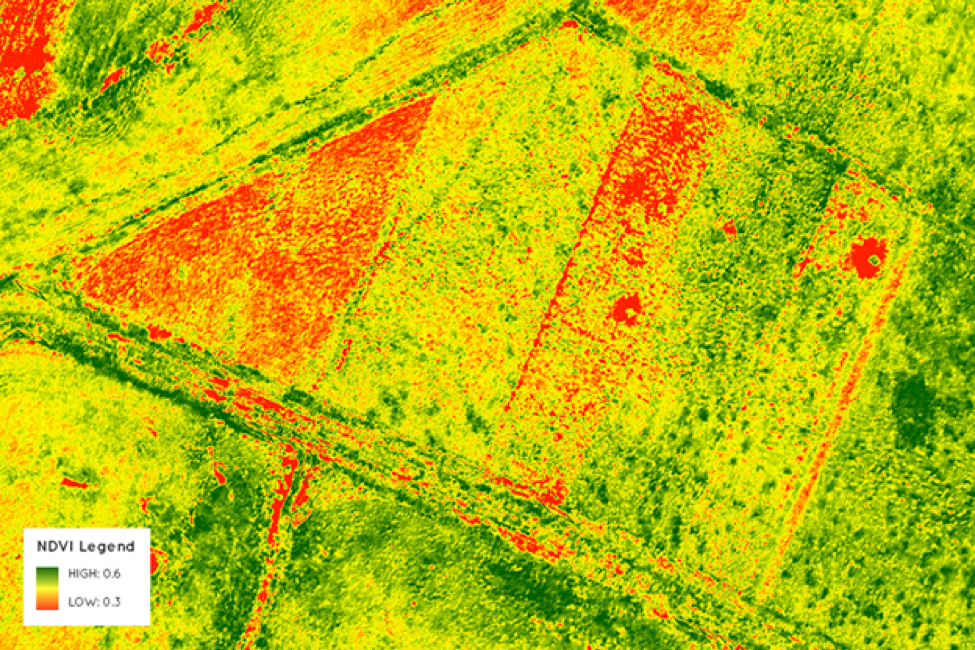
Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) measures the quantity of green vegetation in a spatial region. Experiencing green spaces has many health benefits, including increasing physical activity and improving mental health, as well as improving air quality and mitigating the urban heat island effect.
