Particulate Matter
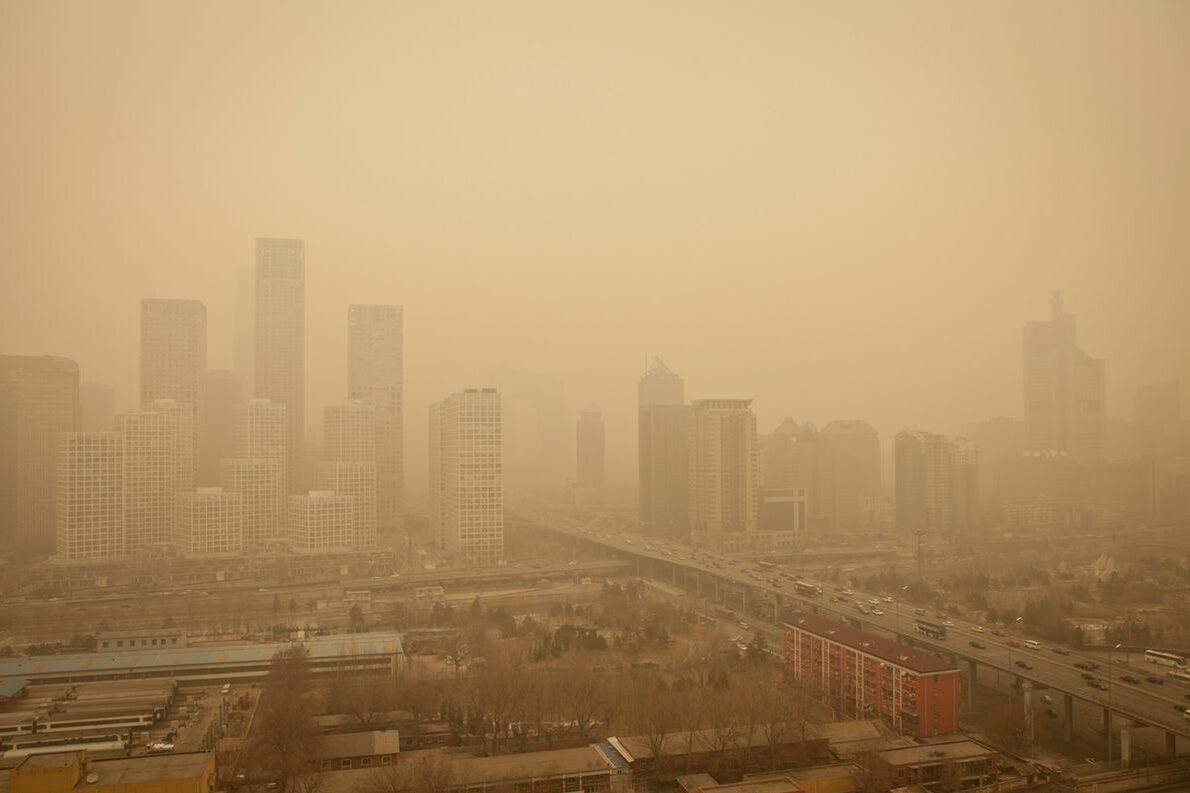

PM2.5 is a component of air pollution that measures small airborne particles. These particles are emitted from natural and manmade sources and infiltrate indoors through cracks in the building envelope. Breathing PM2.5 poses respiratory and cardiovascular health risks, as its small size allows it to travel deep into the lungs and bloodstream.
Extreme Heat
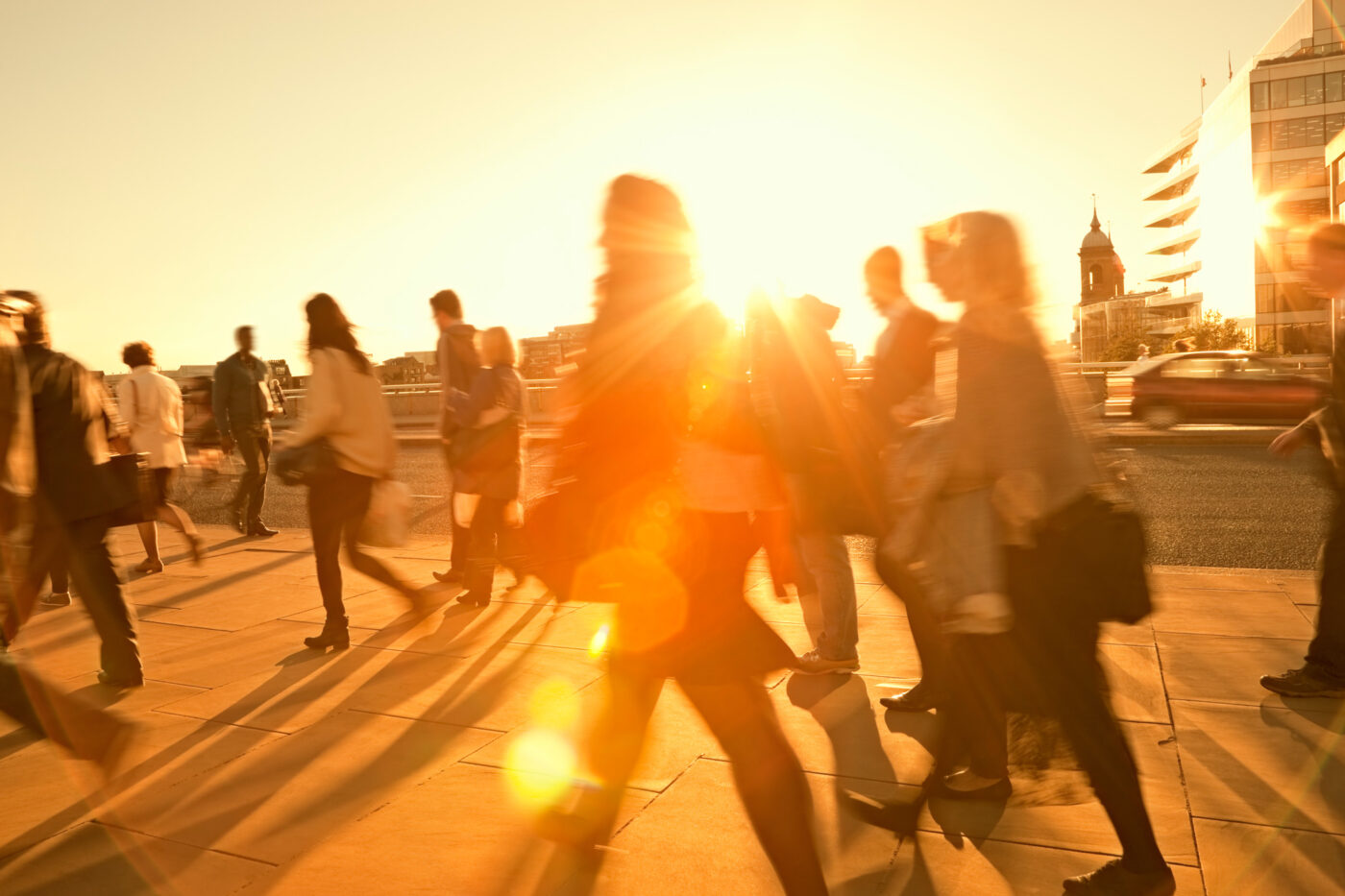

Extreme heat occurs when exceptionally hot and humid weather persists for more than two days and exceed the historical norms for a region. These extreme heat events put enormous stress on our bodies, which may directly cause heat stroke or heat stress and indirectly exacerbate chronic conditions.
Wildfire and Wildfire Smoke
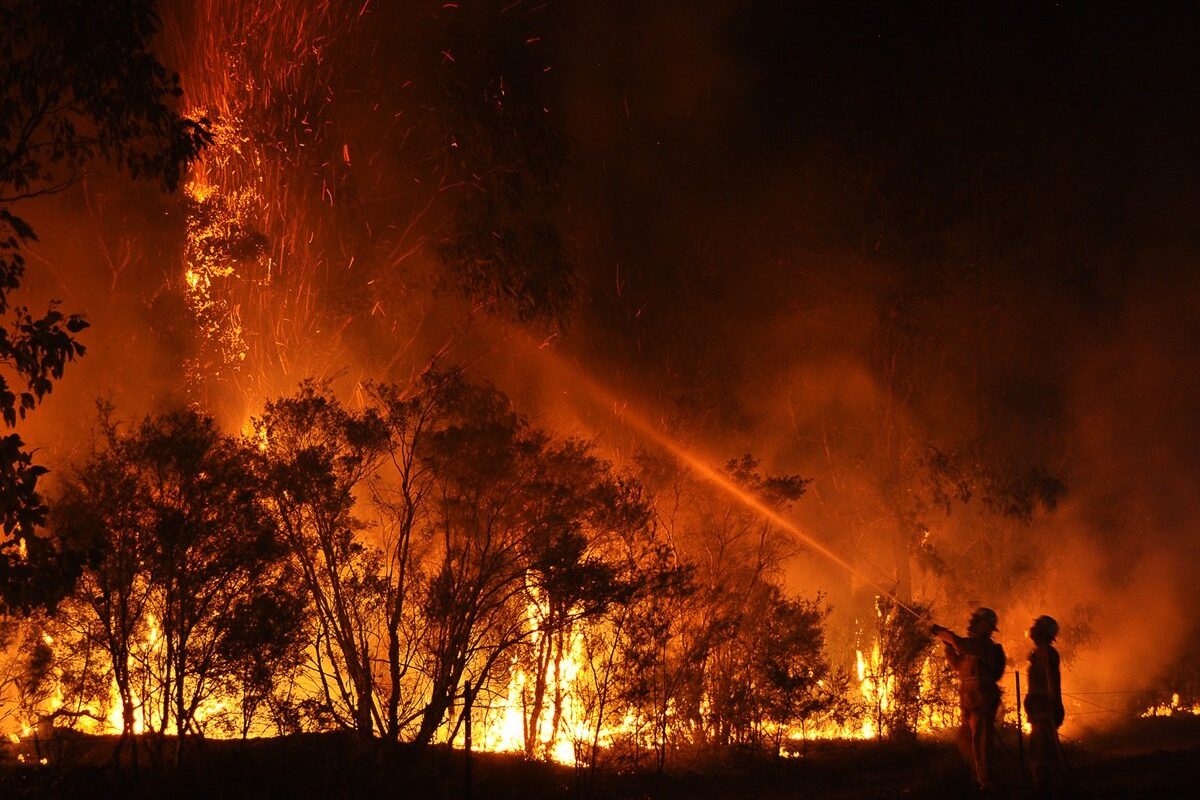

Wildfire is an unplanned, uncontrolled fire burning in a natural area. Wildfires can directly cause immediate human casualties and displacement of affected communities, and indirectly produce high levels of air pollution, which can influence the respiratory and cardiovascular health of the immediate community and distant regions, alike.
Drought
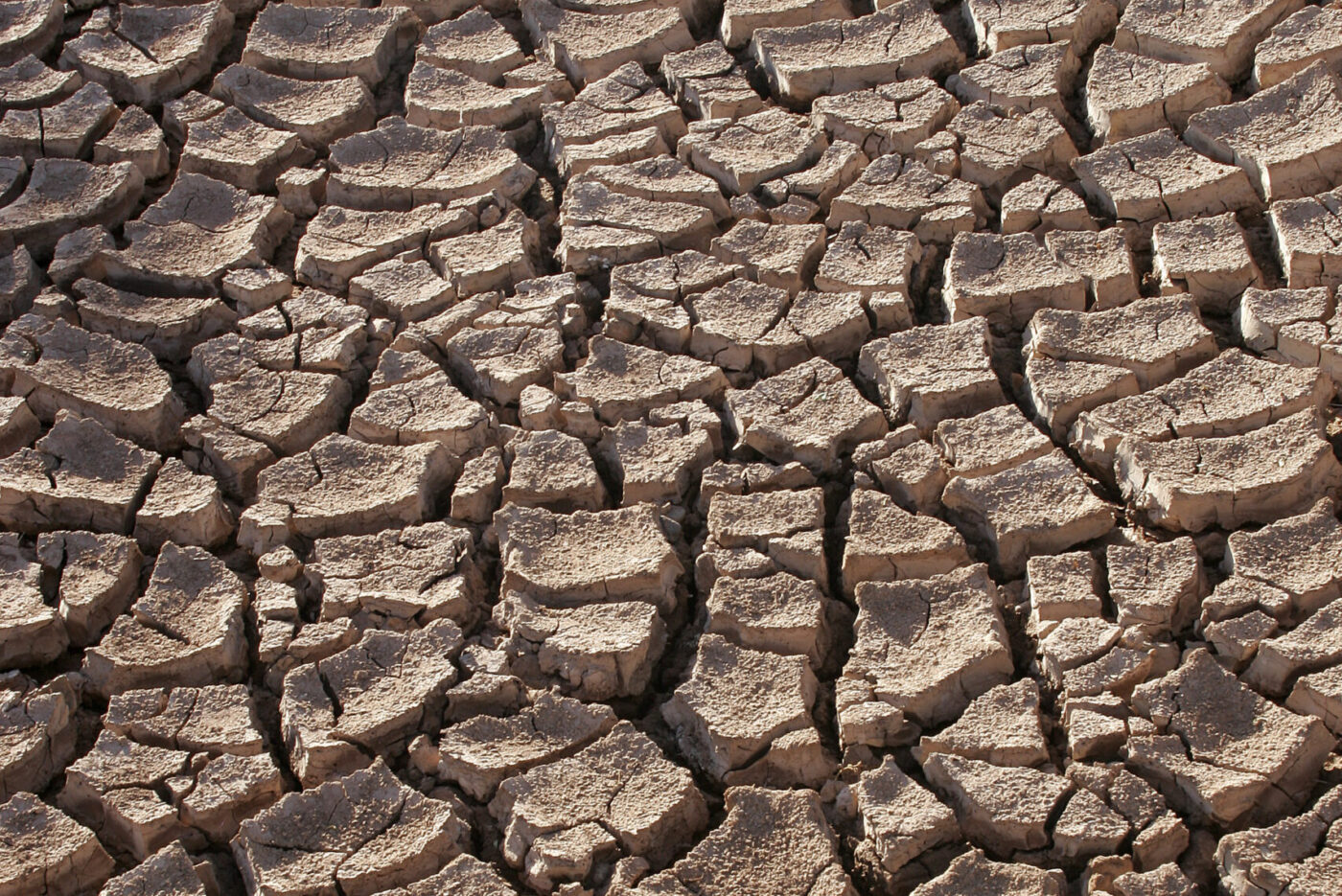

Drought describes abnormally dry weather conditions for a region. Due to the great influence of water in the environment and the socio-economic role of water, the health impacts of droughts span from chronic disease aggravation to infectious disease augmentation, to mental and societal unrest.
Flooding
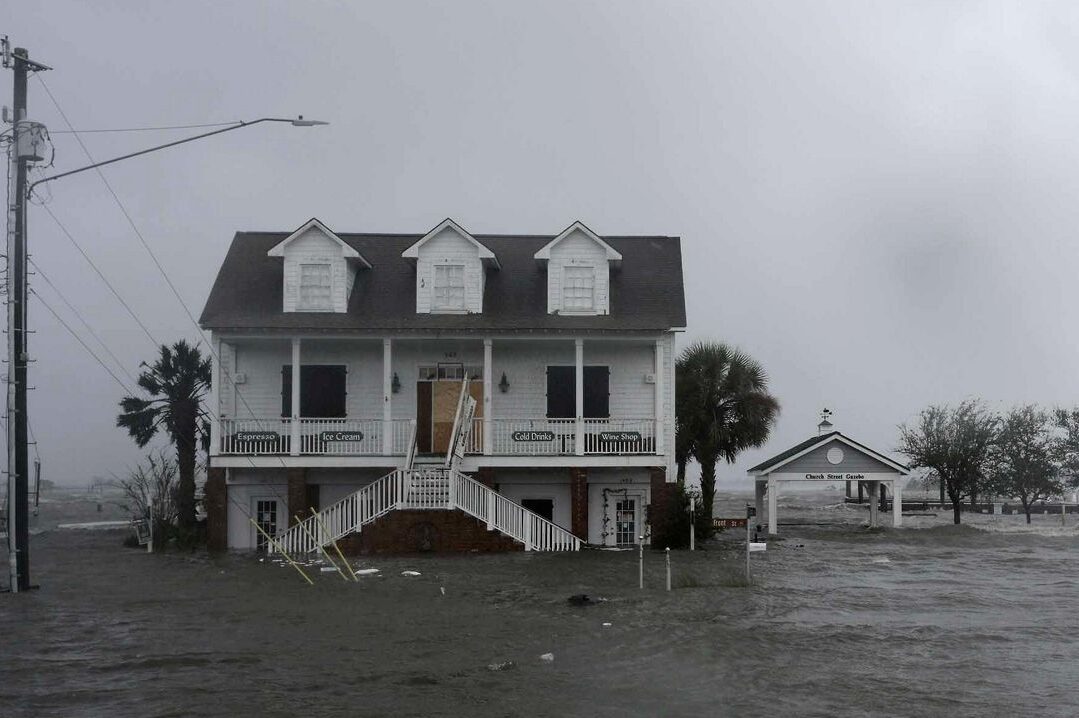

Flooding occurs along the coast and along riverbanks due storm events or anthropogenic climate change trends. Flooding of homes or other community structures impact both our physical and mental health through mold growth, accelerated spread of infectious disease, disruption of community, and displacement of people.
Waste Proximity

Waste proximity indicates the distance and density of facilities managing chemicals that pose risk to our health and ecosystems. Such facilities may introduce pollutants beyond their fence line, meaning that nearby communities breathe more contaminated air, contact more contaminated soil and surface water, and drink compromised water.
Noise Pollution

Noise pollution refers to exposure to a disturbing level of sound that interferes with normal activities or disrupts/diminishes quality of life. While many may consider noise to be just an annoyance, prolonged exposure can disturb our sleep, aggravate stress-related ailments, and contribute to cognitive and psychological issues.
Traffic Proximity
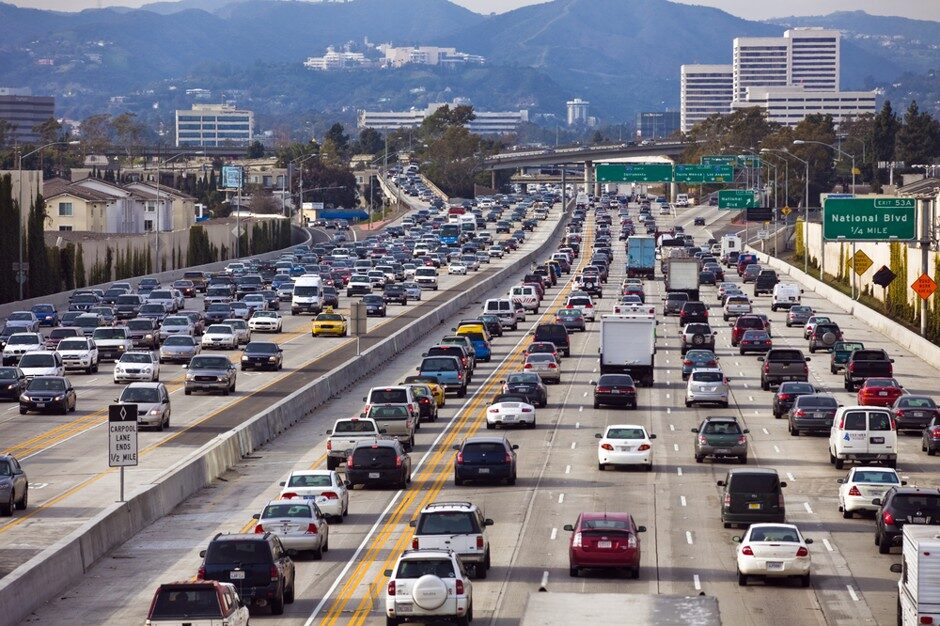

Traffic proximity indicates the distance and density of roadways with the potential to negatively impact health. Due to emissions from automobiles and heavy traffic noise pollution, communities proximal to traffic may breathe more polluted air, contact more contaminated soil, and experience more cognitive stress.
Ozone
Ground-level ozone is a harmful air pollutant formed by chemical reactions between volatile organic compounds and nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight. Breathing ground-level ozone contributes to acute and chronic respiratory problems and increased concentration of green-house gasses in the lower atmosphere.
